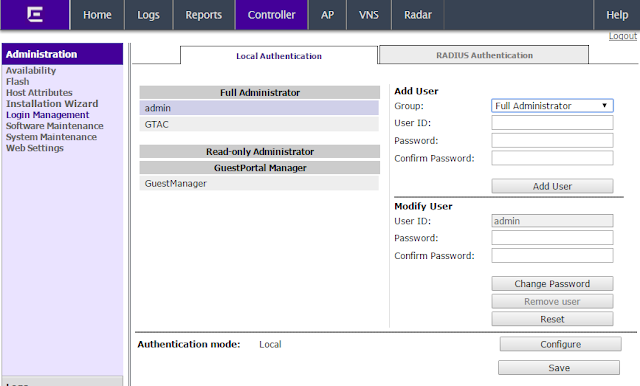
Gain
The gain of antenna provides a change in coverage that is a result of the antenna focusing the area of RF propagation. Amplification of an RF signal will result in gain. An antenna is a device that can change the coverage area, therefore propagating an RF signal further. Antenna gain is measured in decibels isotropic (dBi),which is a change in power as a result of increasing the isotropic energy. Isotropic energy is defined as energy emitted equally in all directions. The sun is a good example of isotropic energy, emitting energy in a spherical fashion equally in all directions. The following shows a drawing of a wireless LAN system with 100 mW of power at the antenna. Because of gain, the antenna emits 200mW of Power.
Above the picture from CWAP
Antenna Polarization
Antenna polarization describes how a wave is emitted from an antenna and the orientation of the electrical component or electric field of the waveform. To maximize signal, the transmitting and receiving antennas should be polarized in the same direction or as closely as possible.
If the polarization of the transmitter and receiver are different, the power of the signal will decrease depending how different the polarization is.
above picture from CWAP